When we pull data from different sources i.e. SQL, txt file, CSV files...., The date columns are imported in text format because of their source data type or could be due to any other reason.
For example - You have data of month in text format with no fixed length(at least three characters) like Jan, Febr, March, Apr, May etc. & you want to convert them into number as 1,2,3,4,5.
In this case, the best formula you can use to convert month in text to number is =Month(A1&1) or =Month("Apr"&1)
I am not sure you are going to use this function directly but you can use it as sub function in Date function as well like
=DATE(2011, MONTH(A1&1),2)
***This formula is submitted by Manoj Kumar in the Group Puzzle. Thanks Manoj.***
If you have any feedback or better solution , Feel free the write the comment.
Excel Daily Tip
You know that Microsoft Excel is a handy program for accomplishing all sorts of tasks. Now, get the scoop on neat little tricks you may not know about. While they probably won't change your life, they'll definitely enhance your productivity. Managed by - Ayush Jain (An excel enthusiast)
Saturday, January 8, 2011
Wednesday, January 5, 2011
Custom Number and Date Format
Click here to read full article on 'Custom' Format.
What is 'Custom Format' ?: Microsoft Office Excel provides many built-in number formats, but in some cases they do not meet our needs, we can customize a built-in number format to create our own.
Why 'Custom Format' and not 'Conditional Formatting'?: because to cure 'Common Cold' we go to doctors not surgeons. Exactly, when there is a simple and robust way then why to go otherwise. There are many benefits of using custom format including these:
1. Less overhead than Conditional Formatting.
2. Values can be used easily in formulas (Less manipulation required).
3. Charts looks better with custom colored labels/axis.
4. Works on all versions of Excel.
and many more which you can figure out using your innovative mind after reading this article.
Examples:
Let's move with some examples of various data. Essentially, examples makes this subject simple.
I - BASIC EXAMPLES
Click here to read full article on 'Custom' Format including intermediate and advanced examples with theory and logic.
What is 'Custom Format' ?: Microsoft Office Excel provides many built-in number formats, but in some cases they do not meet our needs, we can customize a built-in number format to create our own.
Why 'Custom Format' and not 'Conditional Formatting'?: because to cure 'Common Cold' we go to doctors not surgeons. Exactly, when there is a simple and robust way then why to go otherwise. There are many benefits of using custom format including these:
1. Less overhead than Conditional Formatting.
2. Values can be used easily in formulas (Less manipulation required).
3. Charts looks better with custom colored labels/axis.
4. Works on all versions of Excel.
and many more which you can figure out using your innovative mind after reading this article.
Examples:
Let's move with some examples of various data. Essentially, examples makes this subject simple.
I - BASIC EXAMPLES
| COMMENTS | TO DISPLAY | AS | USE THIS |
| Leading Zeros | 26 | 0026 | 0000 |
| Phone Number | 9999404843 | 999-940-4843 | 000-000-0000 |
| Day of the Date | 26/05/1984 | Saturday | dddd |
| Month of the Date | 26/05/1984 | May | mmmm |
| Comma Place holder | 23456789 | 23,456,789 | #, ### |
| Currency | 2605.5 | € 2,605.50 | € #,###.00 |
Click here to read full article on 'Custom' Format including intermediate and advanced examples with theory and logic.
Friday, December 31, 2010
Hide Cell error while printing
If you want to hide the error while printing your spreadsheet, There is a simple print setting change you need to do.
Follow the below steps:-
1) Go to Page Setup
2) Select Sheet tab
3) Select blank or "--" in "cell error as:" option.
4) click Ok and print the page
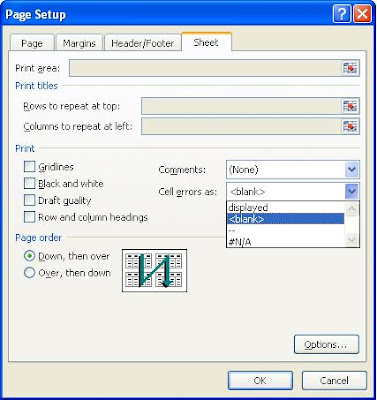
This will keep the error in spreadsheet but will not be displayed on printed pages.
Sometimes it’s useful to know where the errors are so you can correct any that are not expected, but if you regularly print reports you probably don’t want the errors displayed.
Do give a try when next time you print any spreadsheet.
Follow the below steps:-
1) Go to Page Setup
2) Select Sheet tab
3) Select
4) click Ok and print the page

This will keep the error in spreadsheet but will not be displayed on printed pages.
Sometimes it’s useful to know where the errors are so you can correct any that are not expected, but if you regularly print reports you probably don’t want the errors displayed.
Do give a try when next time you print any spreadsheet.
Wednesday, December 29, 2010
3 Things to remember before Excel VBA Job Interview
Like giving interview is a skill, taking interview is another great skill. Ashish Jain have taken many interviews in the past and given more than he has taken and here he is sharing the content from his experience. Your interview experience may be totally different than he has mentioned here but you must be aware of it and should not miss some common things mentioned here. These are his personal views and have nothing to do any of his past or present employers.
If a good interviewer will conduct an interview, he will not probe your technical knowledge only but also how much logical and reasoning thinking you possess along with some programming etiquette. You must remember these 3 things are interviewed in a good Excel and VBA job interview for Analyst position:
1. General Programming Attitude
2. Knowledge of Excel Object Model
3. Excel Knowledge (Data Validation, Subtotal, Formulas etc.)
Read the full article here written by Ashish Jain on eXceLiTems.com
If a good interviewer will conduct an interview, he will not probe your technical knowledge only but also how much logical and reasoning thinking you possess along with some programming etiquette. You must remember these 3 things are interviewed in a good Excel and VBA job interview for Analyst position:
1. General Programming Attitude
2. Knowledge of Excel Object Model
3. Excel Knowledge (Data Validation, Subtotal, Formulas etc.)
Read the full article here written by Ashish Jain on eXceLiTems.com
Tuesday, December 28, 2010
50 Excel VBA Oral Interview Questions
These Excel VBA Interview questions are being posted keeping in mind that reader is aware of working with VBA, have some programming and MS Excel background and is aware of terminologies. This question bank is helpful for both Interviewee and Interviewer as it provides a quick channel of questions and answers covering major topics of Excel and VBA.
If you're looking for a job in MIS/Automation/Dashboard creation etc. as a Business Analyst, Senior Analyst, Associate Analyst, etc involving MS Excel, MS Access, VBA, SQL, Cognos, ASP.NET etc then Click here on 'Excel VBA Job Postings'
Click here to read all the 50 questions and answers.
ByVal: If you pass an argument by value when calling a procedure the variable's value can be changed with in the procedure only outside the actual value of the variable is retained.
ByRef is default: Passing by reference is the default in VBA. If you do not explicitly specify to pass an argument by value VBA will pass it by reference.
i) The Boolean data type has only two states, True and False. These types of variables are stored as 16-bit (2 Byte) numbers, and are usually used for flags.
ii) The Byte data type is an 8-bit variable which can store value from 0 to 255.
iii) The Double data type is a 64-bit floating point number used when high accuracy is needed.
iv) The Integer data type is a 16-bit number which can range from -32768 to 32767. Integers should be used when you are working with values that can not contain fractional numbers. In case, you're working over 32767 rows use Long as data type.
v) The Long data type is a 32-bit number which can range from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
vi) The Single data type is a 32-bit number ranging from -3.402823e38 to -1.401298e-45 for negative values and from 1.401298e-45 to 3.402823e38 for positive values. When you need fractional numbers within this range, this is the data type to use.
vii) The String data type is usually used as a variable-length type of variable. A variable-length string can contain up to approximately 2 billion characters. Each character has a value ranging from 0 to 255 based on the ASCII character set.
i) Forms controls can be used on worksheets and chart sheets. Forms controls can also be placed within embedded charts in Classic Excel (though not in Excel 2007). ActiveX controls can only be used on worksheets. ActiveX controls do not work in MacExcel.
ii) The Forms controls aren’t very complicated, and they have been part of Excel for longer (they were used in Excel 5/95’s dialog sheets) than the Controls Toolbox (Excel 97), so it stands to reason that they’d be more seamlessly integrated. Being newer, the ActiveX controls have richer formatting possibilities. Both can link to cells and ranges in the worksheet.
i) Subroutines never return a value but functions does return values.
ii) A function could not change the values of actual arguments whereas a subroutine could change them.
All the controls in the ToolBox except the Pointer are objects in Visual Basic. These objects have associated properties, methods and events.
A property is a named attribute of a programming object. Properties define the characteristics of an object such as Size, Color etc. or sometimes the way in which it behaves.
A method is an action that can be performed on objects. For example, a cat is an object. Its properties might include long white hair, blue eyes, 3 pounds weight etc. A complete definition of cat must only encompass on its looks, but should also include a complete itemization of its activities. Therefore, a cat's methods might be move, jump, play, breath etc.
Visual Basic programs are built around events. Events are various things that can happen in a program. Let us consider a TextBox control and a few of its associated events to understand the concept of event driven programming. The TextBox control supports various events such as Change, Click, MouseMove and many more that will be listed in the Properties dropdown list in the code window for the TextBox control. We will look into a few of them as given below.
* The code entered in the Change event fires when there is a change in the contents of the TextBox
* The Click event fires when the TextBox control is clicked.
* The MouseMove event fires when the mouse is moved over the TextBox
Click here to read all the 50 questions and answers.
If you're looking for a job in MIS/Automation/Dashboard creation etc. as a Business Analyst, Senior Analyst, Associate Analyst, etc involving MS Excel, MS Access, VBA, SQL, Cognos, ASP.NET etc then Click here on 'Excel VBA Job Postings'
Ques 01. What is the difference between ByVal and ByRef and which is default ?
Solution: ByRef: If you pass an argument by reference when calling a procedure the procedure access to the actual variable in memory. As a result the variable's value can be changed by the procedure.ByVal: If you pass an argument by value when calling a procedure the variable's value can be changed with in the procedure only outside the actual value of the variable is retained.
ByRef is default: Passing by reference is the default in VBA. If you do not explicitly specify to pass an argument by value VBA will pass it by reference.
Ques 02. What is the meaning of Option Explicit and Option Base?
Solution: Option Explicit makes the declaration of Variables Mandatory while Option Base used at module level to declare the default lower bound for array subscripts. For eg. Option Base 1 will make the array lower bound as 1 instead of 0.Ques 03. What are various data type and their size?
Solution:i) The Boolean data type has only two states, True and False. These types of variables are stored as 16-bit (2 Byte) numbers, and are usually used for flags.
ii) The Byte data type is an 8-bit variable which can store value from 0 to 255.
iii) The Double data type is a 64-bit floating point number used when high accuracy is needed.
iv) The Integer data type is a 16-bit number which can range from -32768 to 32767. Integers should be used when you are working with values that can not contain fractional numbers. In case, you're working over 32767 rows use Long as data type.
v) The Long data type is a 32-bit number which can range from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
vi) The Single data type is a 32-bit number ranging from -3.402823e38 to -1.401298e-45 for negative values and from 1.401298e-45 to 3.402823e38 for positive values. When you need fractional numbers within this range, this is the data type to use.
vii) The String data type is usually used as a variable-length type of variable. A variable-length string can contain up to approximately 2 billion characters. Each character has a value ranging from 0 to 255 based on the ASCII character set.
Ques 04. Difference between ActiveWorkbook and ThisWorkbook.
Solution: ThisWorkbook refers to the workbook where code is being written while ActiveWorkbook refers to the workbook which is in active state with active window. In case of only one workbook open, ActiveWorkbook is same as ThisWorkbook.Ques 05. Code to find a Last used Row in a column or Last used column of a Row.
Solution: Last Row in a column can be find using End(xlUp) and Last Column in a row can be find using End(xlToLeft). For e.g. Range("A1048576").End(xlUp).Row gives last used row of Column A.Ques 06. Difference between ActiveX and Form Controls.
Solution: i) Forms controls can be used on worksheets and chart sheets. Forms controls can also be placed within embedded charts in Classic Excel (though not in Excel 2007). ActiveX controls can only be used on worksheets. ActiveX controls do not work in MacExcel.
ii) The Forms controls aren’t very complicated, and they have been part of Excel for longer (they were used in Excel 5/95’s dialog sheets) than the Controls Toolbox (Excel 97), so it stands to reason that they’d be more seamlessly integrated. Being newer, the ActiveX controls have richer formatting possibilities. Both can link to cells and ranges in the worksheet.
Ques 07. What is the difference b/w Functions and Subroutines?
Solution: i) Subroutines never return a value but functions does return values.
ii) A function could not change the values of actual arguments whereas a subroutine could change them.
Ques 08. How to debug a VBA code?
Solution: Using Breakpoints(F9), Step-by-step execution (F8), Debug.Print & Immediate Window and Watch window.Ques 09. Draw basic Excel Object Model.
Solution: Application --> Workbooks --> Worksheets --> Range / ChartQues 10. What are properties, methods, events and objects?
Solution: For details click here --> http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms172576%28VS.80%29.aspxAll the controls in the ToolBox except the Pointer are objects in Visual Basic. These objects have associated properties, methods and events.
A property is a named attribute of a programming object. Properties define the characteristics of an object such as Size, Color etc. or sometimes the way in which it behaves.
A method is an action that can be performed on objects. For example, a cat is an object. Its properties might include long white hair, blue eyes, 3 pounds weight etc. A complete definition of cat must only encompass on its looks, but should also include a complete itemization of its activities. Therefore, a cat's methods might be move, jump, play, breath etc.
Visual Basic programs are built around events. Events are various things that can happen in a program. Let us consider a TextBox control and a few of its associated events to understand the concept of event driven programming. The TextBox control supports various events such as Change, Click, MouseMove and many more that will be listed in the Properties dropdown list in the code window for the TextBox control. We will look into a few of them as given below.
* The code entered in the Change event fires when there is a change in the contents of the TextBox
* The Click event fires when the TextBox control is clicked.
* The MouseMove event fires when the mouse is moved over the TextBox
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)